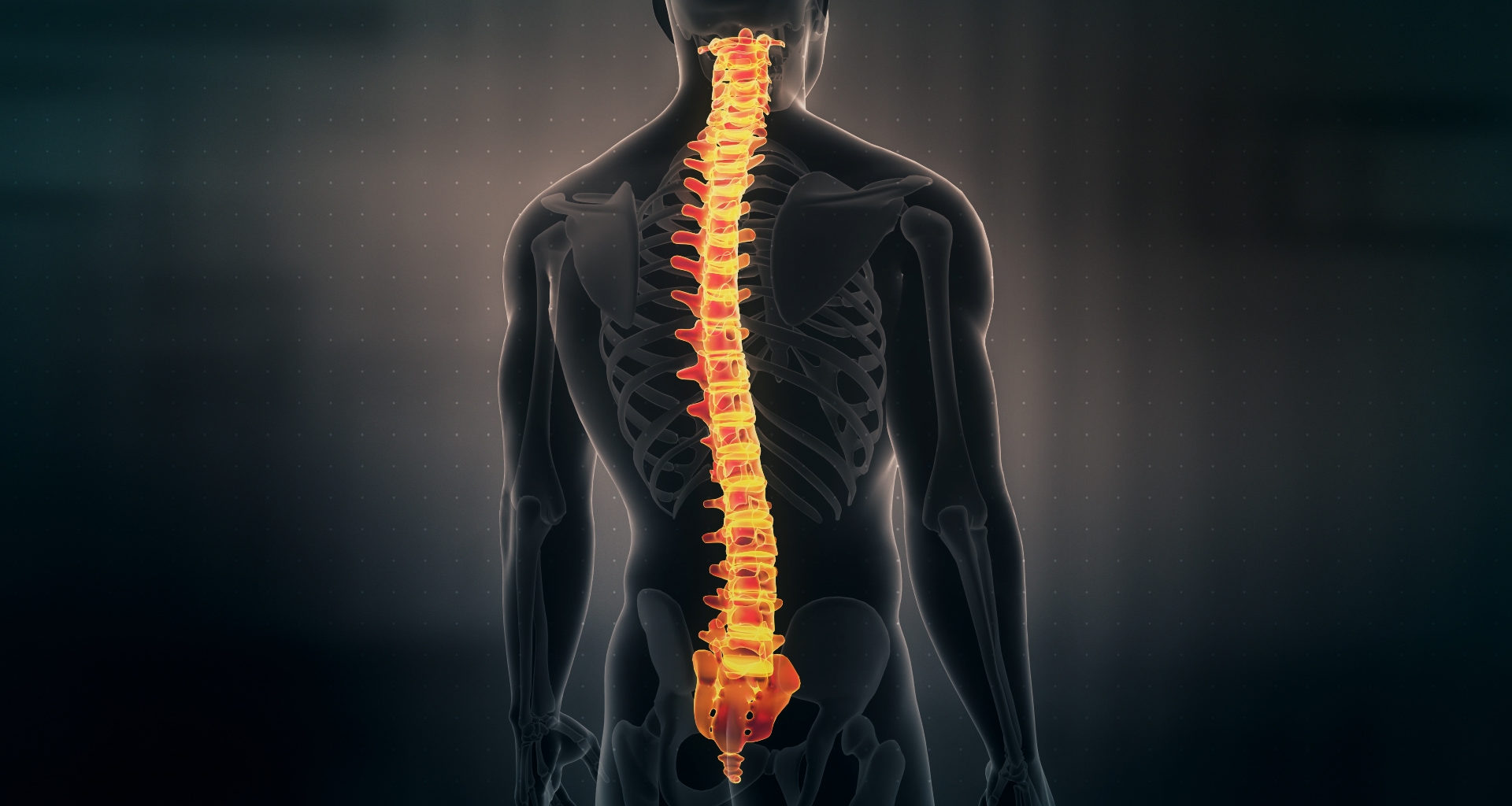
The central nervous system, or CNS, is made up of the spinal cord and the brain. The spinal cord is a long and tubular structure made up of nervous tissue. The core part of the spinal cord is filled with CSF, or cerebrospinal fluid, which is enclosed by the backbone. The shape of the spinal cord is cylindrical or tubular and is about 43 cm in women and 45 cm in men.
Meninges are a protective layer of membranous sheaths that surrounds the spinal cord. The meninges are the pia mater, dura mater and arachnoid mater. These coverings continue to serve as brain coverings.
Anatomy of Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is a continuous structure. They are made up of 31 segments. The spinal nerves which emerge from the spinal cord are responsible for the segmental appearance of the spine. Asymmetrically, 31 pairs of spinal nerves are connected to segments of the spinal cord. The spinal cord typically extends from the brainstem to the backbone or vertebral column. The bones that make up the spinal cord are termed vertebrae, and these are classified into five regions.
- Cervical – The seven movable vertebrae of the neck.
- Lumbar – The five movable vertebrae of the lower back.
- Thoracic – The twelve movable vertebrae in the middle of the back.
- Sacrum – The five joined vertebrae in the pelvic area.
- Coccyx – The four fused vertebrae in the tailbone region.
The vertebrae in all five domains of the vertebral column vary in size and shape. They do, however, have a body, a vertebral arch, and seven processes in common.
In comparison to humans and other higher vertebrates, lower animals have a more complicated spine. A notochord, or rod-like structure, is present in early chordates and serves to support and stiffen the body. All vertebrates develop a notochord, which in adulthood is replaced by the spinal column.
Spinal Cord Injury
A spinal cord injury can result in dysfunction that is either temporary or permanent. The following factors lead to spinal cord dysfunction:
- Direct harm brought on by accidents or gunfire.
- Compression by a disc, bone fragment or haematoma.
- Ischemia is brought on by the rupture of spinal arteries.
During a mechanical injury, the spinal cord may be split in half, one lateral half may be injured, or there may be a widespread crushing of numerous spinal cord segments.
Function of Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is the main coordination centre for reflex actions. It reaches the lumbar region of the backbone from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem. The primary function of the spinal cord is to transport nerve signals all throughout your body. Three vital tasks are accomplished by these nerve signals. They are:
- Autonomic functions – They control your body’s activities and actions. Your movements are controlled by brain signals that are sent to various body components. They also control autonomic (involuntary) processes like your heart rate, breathing rate, and bowel and bladder operations.
- Motor functions – They also control your reflexes. Some reflexes involuntary movements (reflexes) are under the direct control of your spinal cord and not your brain. For instance, your spinal cord regulates your patellar reflex. It is an involuntary movement of the leg when someone kicks your shin (tibia) in a specific spot.
- Sensory functions – Your brain records and processes sensations like pressure or discomfort with the aid of signals from other areas of your body. The spinal cord helps in reporting these senses to the brain.
The quality of life is directly impacted by the condition of the spine and neurological system. Maintaining a strong and flexible back will help you in many activities. Additionally, have a decent posture and consume a nutritious diet because the spinal cord and all of the bone and tissue in the spine require adequate nutrients.